Solutions
Law firms
Tax, audit & accounting firms
Success stories
-
A true competitive advantage
Law firm Zarwin Baum’s embrace of generative AI as the natural next step in the evolution of legal work and their adoption of CoCounsel Legal has helped them achieve remarkable efficiency gains and improved client relationships.
-
Workflow transformation drives impact
Brinks, a global leader in secure logistics and security solutions, used CoCounsel to reimagine what was possible with AI tools, turning legal challenges into a competitive advantage.
-
The forefront of audit tech
A better auditing workflow solution was the answer to multiple challenges faced by The Mercadien Group. Find out how they achieved greater efficiency by embracing Cloud Audit Suite.
Products
Legal
Trade & supply
Tax, audit & accounting
- 1040SCAN
- Audit Intelligence Analyze
- CoCounsel Audit
- CoCounsel Tax
- Ready to Advise
- Ready to Review
- View all
Corporate tax
Recommended products
-
CoCounsel Legal
Transform your work with the only AI legal solution uniting research, drafting, and document analysis in a single experience. Designed by legal experts and built on trusted content and advanced AI, CoCounsel Legal accelerates multistep work so you can better serve your clients and grow your business.
-
CoCounsel Tax
Transform your tax practice with CoCounsel Tax, an AI-powered assistant that combines trustworthy answers, automation, and firm knowledge into one seamless platform. Enhance efficiency, reduce risk, and improve client confidence with CoCounsel Tax.
-
CLEAR
Powerful software designed for law enforcement, compliance, risk, and fraud investigators. Conduct thorough investigations with ease using our intuitive online investigation software. Efficiently, prevent, detect, and solve crime.
Purchase
Buy solutions
Resources
Insights
Events
Product training
Product communities
Developers
Highlights
-
2026 SKILLS showcase
Join weekly sessions to experience in-depth demonstrations of the leading legal AI products while connecting with strategic law firm leaders in knowledge management, innovation, and AI.
-
Ghosts on the ledger
Payroll fraud is a major compliance risk. Learn how payroll analytics and AI-powered tools can help exorcise phantom employees and employers.
-
Future of professionals report 2025
The Thomson Reuters Future of Professionals Report 2025 reveals how AI continues to shape professional work — and what it takes to get ahead. This year’s report shows that increased efficiency, productivity, and cost savings top the list of benefits professionals attribute to AI, making it indispensable for organizations facing rapid change.
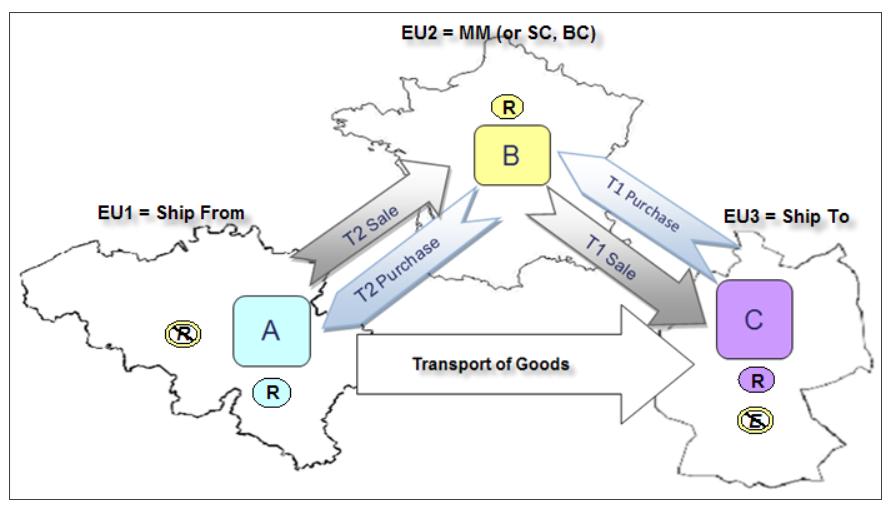
Chain transactions
Triangulation
- A sale of goods.
- 3 taxable persons (ABC) in 3 different EU member states.
- All transactions take place in the EU.
- There are 2 sale transactions: A to B (T2) and B to C (T1).
- 1 transport's directly from A to C, either ship or pickup.
- Establishment of Middleman in the Ship To location (C) depends on the authority option (country specific rule.)
Regulations governing triangulation simplification
- The acquisition of goods gets made by a taxable person who isn't established in the concerned member state but is identified for VAT purposes in a different member state.
- The acquisition of goods gets made for the purposes of the subsequent supply of these goods, in the concerned member state, by the taxable person in A.
- The goods acquired by the taxable person are directly dispatched or transported from a member state other than that in which he's identified for VAT purposes.
- The person to whom the goods are supplied is another taxable person, or a non-taxable legal person, who's identified for VAT purposes in the concerned member state.
- The person to whom the goods are supplied has been designated as liable for payment of the VAT due on the supply carried out by a taxable person who's not established in the member state where tax is due.
Type | All member states | Country-specific conditions |
|---|---|---|
Registration / establishment | Each company uses a registration in a different EU country: A in EU1, B in EU2, and C in EU3 | Option 1: B mustn't be established in EU3 or B mustn't be registered in EU1 or
|
Transportation | Goods must be transported directly from EU1 to EU3 | A or B must arrange transport or
|
Evaluating triangulation simplification
Example 1 | Role | Registration |
|---|---|---|
Sales Unit (B) | Middleman | MM (SF, ST) |
End Customer (C) | Buyer | ST |
Warehouse (A) | Seller | SF |
Example 2 | Role | Registration |
|---|---|---|
Sales Unit (B) | Seller | SP (SF, ST) |
End Customer (C) | Buyer | ST |
Warehouse (A) | N/A | Assumed to be registered in SF |
Example 1 | Role | Registration |
|---|---|---|
Sales Unit (B) | Middleman | MM (SF, ST) |
End Customer (C) | Buyer | ST |
Warehouse (A) | Seller | SF |
Example 2 | Role | Registration |
|---|---|---|
Sales Unit (B) | Buyer | BP (SF, ST) |
End Customer (C) | N/A | Assumed to be registered in ST |
Warehouse (A) | Seller | SF |
This article applies to:
- Product: ONESOURCE Determination,ONESOURCE Indirect Tax
