Example 3 - pay items
Hourly rate - total hours
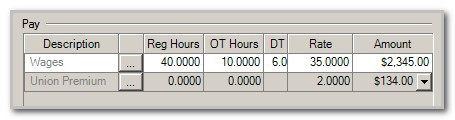
In this example, the employee receives regular wages (which use the Hourly rate calculation method) plus a Union Premium Pay amount (which uses the Hourly rate - Total hours calculation method).
During this pay period, the employee worked 40 regular hours, 10 overtime hours, and 6 double-time hours. The application totals the hours as follows.
Hours worked | Hours x multiplier | Total hours |
|
|
6 Double-time | 6 x 2.0 | 12.00 |
|
When you enter wage hours for the employee, the application automatically calculates the Union Premium Pay (67 hours x $2) as a separate payroll item when the wage hours are entered.
You can modify the calculation of the payroll item in various ways by selecting items to be excluded, such as by marking the
Premium wages
checkbox in the Exclusions section.
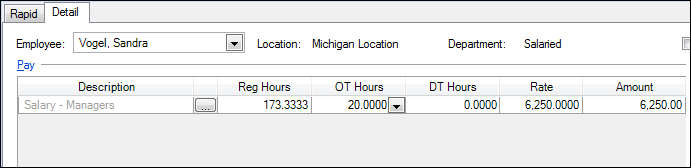
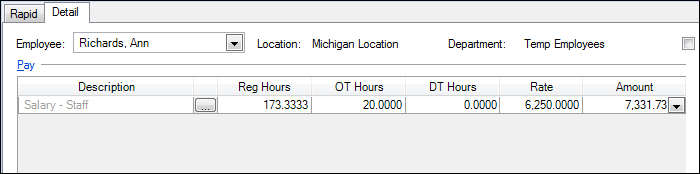
In this example, the employee’s annual pay (Salaried – Hours sensitive calculation type) is $75,000.00, and she is on a Monthly payroll schedule. Her monthly pay rate, then is $6,250.00. The employee worked 20 hours of overtime during this payroll period. Adding these hours during payroll check entry increases her pay amount to $7331.73, although her rate is still $6, 250.00.
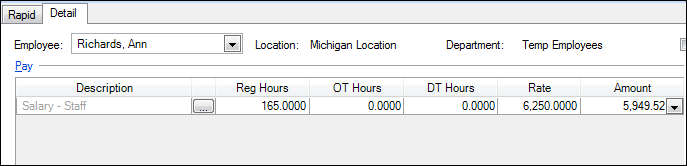
When this employee works fewer than the required hours, her pay amount decreases to $5,949.52, although her rate is still $6, 250.00.
In this example, the employee’s pay item (Salary – Managers) uses the Salary calculation type. Her salary amount is $75,000.00 and she is on a Monthly payroll schedule. Accounting CS divides the salary amount into 12 payments of $6,250.00. The employee worked 20 hours of overtime during this payroll period, but adding those hours during payroll check entry does not change her pay amount.