Blockchain distributed ledger technology is poised to transform the tax and accounting industry
The advent of cloud-based accounting systems has proven to be game-changing. Even the cloud itself, however, could pale in comparison to blockchain technology, which is potentially one of the most disruptive technologies to affect the entire business world.
According to The World Economic Forum, 80 percent of banks are predicted to start blockchain projects this year, and US$1.4 billion has already been invested in the technology over the past three years.
What is blockchain?
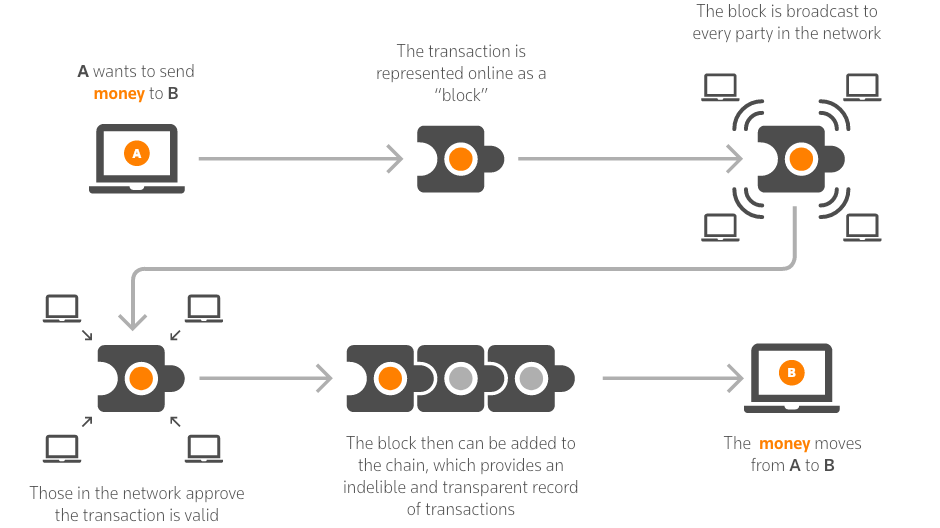
A blockchain is a distributed, decentralized ledger that lets information be viewed but not copied or altered. Originally designed to facilitate transactions using the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, blockchain is a distributed database. There is no central version of blockchain: it lives across a network of computers. This makes it incredibly secure, since a hacker can’t access all instances of the blockchain.
Blockchain stores records in groups called blocks. Each block is time-stamped and linked to the previous block. It’s incorruptible and unalterable, making it ideal for recording transactions without requiring a central authority.
What makes distributed ledgers so disruptive?
Information contained in a distributed ledger is updated in real-time, and it’s permanent, so no one can delete the information. All the information is publicly viewable, so the blockchain is completely transparent.
Importantly, because blockchain lets participants verify and audit transactions without the need for a third party, it delivers a level of certainty and trust not seen previously in internet-based transactions. It practically automates parts of the audit process, for example.
What industries will be affected?
The accounting industry is likely to experience the most disruption as the result of blockchain technology, since it fundamentally changes the way transactions are made and recorded. But blockchain, because it removes the need for a third party or middleman, has exciting potential applications outside of financial transactions.
Some of the industries likely to be disrupted by blockchain include:
Healthcare
Providers will be able to share medical records securely using a private or permission-restricted blockchain, relying on the security inherent in blockchain to ensure no information has been altered.
Politics
Casting, tracking, and counting votes using blockchain will eliminate voter fraud and questions of legitimacy, since the records are open and people can verify the count themselves. The audit trail means officials can be certain that no votes were changed or removed, and no illegitimate votes were added.
Human resources
Employers can check academic records stored in the blockchain to confirm people have actually earned the accreditation they’re claiming.
Entertainment
Blockchain technology could be used to make music sharing fairer and to solve licensing issues. Users could listen to music and use the blockchain to pay artists directly. This could eventually lead to the demise of record companies as we know them.
Real estate
Purchasing and selling properties could become much faster and more streamlined by using blockchain technology instead of manual, extensive paperwork. Real estate blockchain applications can manage the entire process from end to end.
So how will blockchain disrupt the accounting industry?
Blockchain distributed ledger technology will make certain accounting practices and even some professional services obsolete.
For example, once transactions are entered into the blockchain, they can’t be altered. Corrections can be made after the fact, but they are transparent to all parties so data can’t be falsified or manipulated. This makes auditing easier and more reliable, and reduces the possibility of error. Consequently, some of the manual tasks involved in auditing may disappear, although it’s unlikely auditors will be completely replaced.
Also, the transaction in the blockchain is verified, so it eliminates the need for both parties to enter the transaction into their own ledgers. Alternatively, it may lead to a triple-entry system where transactions are entered into both parties’ ledgers as well as into the blockchain.
Security may also be easier to manage using blockchain technology, because it makes financials all but impervious to hacks. This is due to the exceptionally strong security provided by blockchain encryption and the fact that you can’t simply hack into the blockchain and make undetected, unauthorized changes.
How can accountants prepare for blockchain technology?
It’s not a matter of whether blockchain technology will become pervasive; it’s a matter of when. It’s essential for the tax and accounting industry to become familiar with the blockchain and how it works.
If your business depends on audit or other transactional services, consider diversifying into areas that are more creative, because the blockchain will make the audit process streamlined, fast, and automated. Accountants can add more value by providing strategic advice than by undertaking basic bookkeeping functions and the emergence of blockchain technology should accelerate firms’ evolution away from these tasks.
There are still many unanswered questions about blockchain and how it will be adopted, so accountants and auditors should make themselves part of that conversation to help drive the industry’s direction.
Learn more
Get the latest insights on tax technology developments from our Tax & Accounting business.






